A Non-Technical Introduction to Solar Power
There are four primary components to solar electric power systems. Known also asa "solar power system", they include solar panels, charge controllers, batteries and inverters. All of these components are necessary to have of the two types of solar electric systems, grid-connected and off-grid, which we'll discuss in a bit more detail below. These systems are, depending on where you are or the formality of the discussion, referred to as "photovoltaic systems" and also as "solar power systems". The term "photovoltaic" means electricity from light and is often shortened to "PV".
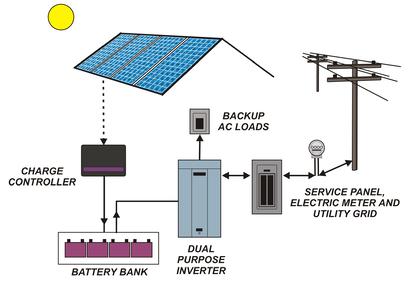 The solar panel is the cornerstone of the solar electric power system. The solar panel(s) acts as a battery charger. When several solar modules are wired together a "solar array" is created. The size of the solar array determines the amount of power that will be produced by the system.
The solar panel is the cornerstone of the solar electric power system. The solar panel(s) acts as a battery charger. When several solar modules are wired together a "solar array" is created. The size of the solar array determines the amount of power that will be produced by the system.
A charge controller is an important system component that regulates the voltage generated from your renewable energy system and properly maintains your batteries. It protects your batteries from being over and under charged, and ensures maximum battery life.
Batteries are used to store the energy that is created by your solar power system. Typically, loads receive their power from batteries instead of directly from the output of a solar panel. A solar panel produces a high voltage that will damage electronics if loads are powered directly. Batteries will provide you with the energy you need at night.
The last major component is the solar inverter, or just inverter. An inverter converts the DC (Direct Current) energy stored in your batteries and turns it into the AC (Alternating Current) power you use in your home. Inverters are rated by wattage and the quality of their output. You can use a 50 watt inverter that plugs into your car 12 volt outlet to power a computer, or you could have a 4000 to 1,000 watt inverter system that powers your home.
These major components can be put together in many different ways. Minor components like wire, disconnects, circuit breakers, and fuses are also needed for a complete system.
Solar Power System Configurations
Stand Alone or "Cabin" Systems
This type of system is most often referred to as an "off-grid solar power system" and there are two way to configure them:
Solar > Charge Controller > Battery > Inverter > AC Loads
or
Solar > Charge Controller > Battery > DC Loads
A stand-alone off-grid solar power system is a system that is not connected to the main electric utility grid. Stand-alone solar electric systems are used when utility power is not available or is too costly to bring in from the nearest access point on the grid. If you have an out-building that is distant from your ranch house, if you own a cabin in the mountains, or a remote summer or winter home beside a remote lake, this type of solar power system can often be the most cost-effective method of providing power to your off-grid location when compared to having power lines installed.
The pro(s) of this type of system are:
- You will not have to rely on the utility grid for power.
- You will save money by not having an electric utility bill because you are producing your own electricity.
The con(s) of this type of system are:
- Even though there will be a cost savings over running utility lines to your location, there is a need for the initial upfront investment.
- You have to know exactly what your electricity requirements are and have the system designed correctly since you don’t have utility power for backup.
- Diesel or gasoline backup systems require fuel and make noise
Grid-Tie Solar Power Systems
Solar > Inverter > Utility
This type of solar power system is connected directly to the main power grid and utilizes an inverter that does not require batteries. During the day, the electricity generated by a grid-tie solar system is fed directly into the utility grid. If you are producing more power then you are using, your meter can even spin backwards. Due to the simplicity of the system, it has the lowest cost per watt. The downfall of this system is that when the utility grid fails the system will also shut down.
So, what can be done to assure that you will still have power when the main power grid fails due to a storm or other mishap? Continue reading...
Grid-Tied Battery Backup System with Solar
This type of system is used to power your home or business and is also used to charge a battery bank. When the batteries are full the excess power is fed back into the grid. In the event of an outage, your critical loads are powered by the system, and the solar panels continue to charge the batteries. The benefit of this system is that you have the ability to sell power back and have the piece of mind that you critical loads will continue to operate no matter if the grid goes down.
Battery Backup System
Utility > Battery Charger > Batteries—Inverter > AC Loads
This is a system that does not involve solar power. This system utilizing an inverter that has a built in battery charger. It will charges batteries and hold them at 100% waiting for a power outage or a brownout. Your critical loads will never see the power outage. Computers, home health equipment, and lights will continue to operate when the utility grid fails. This is a system that is great for areas where power is lost for short periods of time. The limit on this system is the amount of battery capacity that you have. The larger the batteries the longer your run time will be.
Previous | Next | Back To FAQs
